CNC milling is an exceptional technique to produce high quality precision parts in the modern manufacturing era. But it’s not one singular technique that dominates all the machining aspects. There are several different types. You may have heard of face milling or end milling.
Picking the right type of CNC milling is crucial to get the highest level of precision in your projects. That’s why, here we have a comprehensive guide to 12 types of CNC milling operations in precision machining.
Go through the guide, learn the perfect milling process, and get highly precise parts in all your CNC milling projects.
What is CNC Milling?

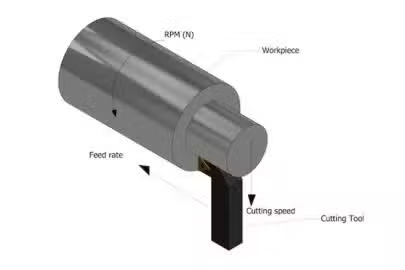
CNC milling is a computer-controlled manufacturing process that uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece, shaping it into the desired form.
The technique relies on pre-programmed instructions to automate the entire process. This level of automation allows for greater precision, consistency, and efficiency in producing complex parts and components.
Core programming of CNC Milling
Programming the CNC milling process requires you to understand the basics of G-code and M-code. These are numerical control codes used to program CNC machines.
- G-code: These codes control the movement of the machine’s axes, such as X, Y, and Z, and other functions like feed rate and spindle speed. For example, G01 is used for linear interpolation, while G02 and G03 are used for circular interpolation.
- M-code: These codes control miscellaneous functions of the machine, such as spindle on/off (M03, M04), coolant on/off (M07, M08), and program end (M30).
Types of CNC Milling Operations
Now, let’s dig deep into the different types of CNC milling operations used in modern machining.
Face Milling

Face milling is a CNC milling operation that involves using a cutting tool with a flat or slightly angled face, typically used to machine the top or bottom surface of a workpiece. Face milling aims to create a flat, smooth, and parallel surface, often as the first step in a more extensive machining process.
Features
- Surface Grid Mapping: A system that creates a digital topography map of the workpiece surface to compensate for flatness deviations.
- Corner Flow Integration: Unique corner approach strategy that eliminates common face-milling witness marks through spiral entry motions.
- Thermal Pattern Recognition: Monitors and adjusts for thermal growth patterns specific to large surface face milling operations.
- Surface Finish Prediction: Analyzes cutter marks and generates optimal feed patterns for achieving specific surface finish requirements.
- Cross-Hatch Prevention: Automatically varies cutter path angles to prevent common face milling cross-hatch patterns.
Plain Milling

Plain milling, also known as slab milling, is a CNC milling operation that focuses on removing material from the sides of a workpiece, creating flat, parallel surfaces. This technique is commonly used for cutting grooves, slots, and other features that run perpendicular to the workpiece’s length.
Features
- Bi-Directional Load Distribution: Alternates cutting direction to balance tool wear specific to long, straight cuts.
- Step-Over Pattern Recognition: Creates optimal step-over distances based on material hardness and desired surface pattern.
- Linear Compensation Mapping: Adjusts tool path to compensate for straightness deviations in long workpieces.
- Pass Depth Sequencing: Calculates optimal depth sequence for rough and finish passes based on material properties.
- Surface Blending Control: Ensures smooth transitions between adjacent passes in wide surface cuts.
Angle Milling

Angle milling is a CNC milling operation that involves the use of a cutting tool with an angled face, allowing for the creation of inclined or angled surfaces on the workpiece. This technique is often employed in the production of beveled edges, chamfers, and other angular features.
Features
- Dynamic Angle Compensation: Intelligent system that maintains precise angles by automatically adjusting for tool wear and deflection during cutting.
- Path Generation Control: Advanced tool path optimization that creates smooth entry and exit movements for clean angle transitions.
- Multi-axis Synchronization: Sophisticated control system that coordinates multiple axes to create precise compound angles.
- Real-time Angle Measurement: Continuous monitoring system that verifies and adjusts cutting angles during operation.
- Variable Angle Optimization: Smart path planning system that automatically adjusts cutting parameters for changing angle surfaces.
Form Milling

Form milling is a CNC milling operation that utilizes a specialized cutting tool with a pre-shaped profile, allowing for the creation of complex geometric features and contours on the workpiece. This technique is beneficial for producing intricate shapes, such as those found in molds, dies, and other specialized components.
Features
- 3D Profile Recognition: Intelligent system that analyzes complex shapes and automatically generates optimal cutting strategies.
- Contour Error Compensation: Advanced monitoring system detects and corrects deviations from programmed contours in real-time.
- Dynamic Tool Point Control: Sophisticated system that maintains precise tool positioning for complex profile cutting.
- Automated Form Validation: A real-time measurement system verifies form accuracy during machining.
- Feature Recognition: Smart system that identifies part features and automatically selects optimal cutting strategies.
Side Milling

Side milling is a CNC milling operation that focuses on removing material from the sides of a workpiece, creating features such as slots, grooves, and steps. This technique is often used with other milling operations to produce more complex part geometries.
Features
- Wall Straightness Monitoring: Continuous measurement system that monitors and compensates for wall deflection during cutting.
- Trochoidal Path Generation: Advanced tool path system that creates smooth, circular movements for efficient deep slot cutting.
- Chip Load Optimization: Intelligent system that adjusts cutting parameters to maintain consistent chip evacuation during side cutting.
- Corner Radius Control: Smart compensation system automatically adjusts tool paths to maintain precise corner radii.
- Wall Deflection Correction: A real-time monitoring system adjusts cutting forces to prevent thin wall distortion.
Straddle Milling
Straddle milling is a CNC milling operation that involves using two cutting tools mounted on the same spindle, allowing for the simultaneous machining of parallel surfaces on a workpiece. This technique is often used to create exact and efficient features like slots, grooves, and steps.
Features
- Dual Cutter Synchronization: Advanced control system that maintains precise alignment between two opposing cutters during operation.
- Parallelism Adjustment: Intelligent system that continuously monitors and adjusts tool positions to maintain parallel surfaces.
- Gap Control System: Sophisticated measurement system that maintains precise spacing between opposing cutters.
- Force Balancing: Smart system that equalizes cutting forces between tools to prevent workpiece distortion.
- Matched Wear Compensation: Advanced monitoring system that adjusts for tool wear to maintain symmetrical cutting.
End Milling

End milling is a CNC milling operation that utilizes a cylindrical cutting tool with flutes on the end, allowing for the creation of features like pockets, slots, and profiles. This technique widely produces complex parts and components across various industries.
Features
- Helical Interpolation: Advanced control system that creates precise helical tool paths with variable pitch for complex pocket features.
- Pocket Optimization: Intelligent system that automatically identifies islands and generates efficient tool paths around them.
- Load Reduction Control: Smart system that modifies corner approaches to maintain consistent tool loads.
- Rest Machining Detection: Advanced material recognition system that identifies unmachined areas and automatically generates clean-up tool paths.
- Feature-based Pathing: A sophisticated system that automatically analyzes part features and automatically generates optimal cutting strategies.
Gang Milling

Gang milling is a CNC milling operation involving multiple cutting tools mounted on the same spindle, allowing for the simultaneous machining of various features or surfaces on a workpiece. This technique is often employed in high-production environments to increase efficiency and throughput.
Features
- Multi-tool Control: Advanced synchronization system that coordinates multiple cutting tools with independent feed rates.
- Tool Spacing Optimization: Intelligent system calculates and maintains optimal spacing between multiple cutters.
- Dynamic Load Distribution: Smart system that balances cutting forces across multiple tools to optimize material removal.
- Sequence Optimization: A sophisticated planning system that determines the most efficient order of operations for multiple features.
- Tool Interaction Management: Advanced monitoring system that prevents tool interference while maximizing cutting efficiency.
Saw Milling

Sawmilling is a CNC milling operation that utilizes a thin, circular saw blade to create features like grooves, slots, and other linear cuts on the workpiece. This technique is beneficial for materials prone to cracking or deformation, as the thin saw blade can minimize the stress on the workpiece.
Features
- Feed Modulation: Intelligent system that automatically adjusts feed rates when cutting through varying material thicknesses.
- Blade Deflection Control: Advanced monitoring system compensating for blade movement during deep cuts.
- Depth Progression: Smart system that optimizes cutting depth increments for efficient material removal.
- Vibration Suppression: A sophisticated monitoring system adjusts cutting parameters to minimize blade vibration.
- Interrupted Cut Control: Advanced system modifies approach strategies for inconsistent or interrupted surfaces.
Thread Milling

Thread milling is a CNC milling operation used to create internal and external threads on a workpiece. This technique is beneficial for producing threaded features that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional tapping or threading methods.
Features:
- Profile Compensation: Intelligent system that maintains accurate thread profiles by adjusting for tool wear and deflection.
- Thread Entry Optimization: Advanced system calculates optimal lead-in and lead-out paths for various thread types.
- Multi-start Synchronization: Sophisticated control system that coordinates multiple thread starts for complex threading operations.
- Pitch Monitoring: A real-time measurement system ensures consistent thread pitch throughout the cutting process.
- Chip Evacuation: Smart system that optimizes tool paths to ensure efficient chip removal during threading operations.
Helical Milling

Helical milling is a CNC milling operation involving a cutting tool with a helical flute, allowing you to create spiral or helical features on the workpiece. This technique is often used in the production of features like internal and external threads, as well as complex sculptured surfaces.
Features:
- 3D Interpolation: Advanced control system that generates precise helical movements with variable pitch and diameter.
- Helix Angle Control: Intelligent system that maintains accurate helix angles throughout the cutting process.
- Multi-start Recognition: Sophisticated system that automatically identifies and generates appropriate paths for multi-start features.
- Parameter Optimization: Smart system that adjusts cutting parameters to maintain consistent helix geometry.
- Entry Strategy Generation: Advanced system that creates smooth entry and exit moves for helical features.
Plunge Milling

Plunge milling is a CNC milling operation that involves the use of a cutting tool that moves perpendicular to the workpiece, allowing for the creation of features like holes, pockets, and slots. This technique is often used in the production of components with complex internal geometries that would be difficult to access using other milling methods.
Features
- Depth Optimization: Intelligent system that calculates optimal plunge depths based on material conditions and tool capabilities.
- Chip Evacuation Control: Advanced system that coordinates, retracts, and dwells to ensure efficient chip removal.
- Peck Cycle Management: Sophisticated system that optimizes pecking depths and frequencies for efficient deep hole creation.
- Force Monitoring: Smart system that adjusts plunge parameters based on real-time cutting force feedback.
- Position Optimization: Advanced system that calculates optimal tool positions for multiple plunge operations.
Key Considerations for CNC Milling Operations

When selecting the appropriate CNC milling operation for your precision machining needs, there are several key factors to consider:
Part Geometry
Evaluate the complexity and specific requirements of the part you need to produce, and choose the milling operation that is best suited to creating the desired features and geometries.
Material Properties
Consider the properties of the workpiece material, such as hardness, brittleness, and machinability, to ensure that the selected milling operation can effectively and efficiently remove material without causing damage or excessive wear on the cutting tools.
Production Volume
Assess your production needs, whether it’s a small, one-off part or a high-volume run, to determine the most cost-effective and efficient milling operation for your specific requirements.
Tool Availability and Compatibility
Ensure that you have access to the specialized cutting tools and equipment required for the selected milling operation and that they are compatible with your CNC machine.
Programming and Setup Complexity
Evaluate the level of complexity involved in programming and setting up the CNC milling operation, as this can impact the time and resources required for each production run.
Throughput and Efficiency
Consider the productivity and efficiency of the milling operation, as this can have a significant impact on your overall manufacturing costs and lead times.
Conclusion
Well, now that you know the 12 different CNC milling operations, you can easily decide which is perfect. The features and details of each technique should help you figure that out. And if you face issues, you can always refer to the consideration factors we shared here.
But if you don’t want to bother about all that and want an expert solution immediately, then Zintilon has your back. They provide all the CNC milling solutions with unmatched quality and expertise.
Great, Together