CNC turning has made it easier to machine parts that would have been challenging decades ago. This technique is accurate and ensures consistency when producing high-quality parts. It uses a stationary cutting tool to remove material from a rotating workpiece. As a result, it produces components of different shapes and sizes that meet stringent specifications and tolerances.
It is crucial to understand the fundamentals of precision CNC turning to maximize its advantages and boost productivity. This article has all the answers to CNC turning questions. It will explain the turning manufacturing process in-depth, the types of operations you can use, and the applications of CNC-turned parts in manufacturing industries.

What Is CNC Turning?
CNC turning is a subtractive machining process that removes material from a workpiece that spins at a high speed. The workpiece is attached to a chuck that makes a varying number of revolutions per minute. As the cutting tool comes in contact with the rotating workpiece, it removes material and sculpts the desired shape. CNC turning machines work with mainly cylindrical or oblong components. It can also be used to manufacture other shapes such as discs, picture cones, hexagons, or a mix.
How To Operate a CNC Turning Machine
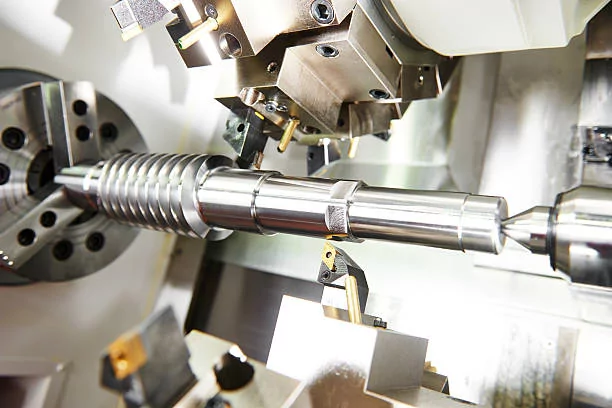

The turning manufacturing process is straightforward. It occurs in 4 stages
Creating a CAD Model
The first step of CNC turning is to prepare a 2D or 3D model of the final design using CAD software. There are many types of software one can use. SOLIDWORKS, Fusion 360, and AutoCAD are the most common. It is easy to prepare CAD models for simple designs. However, more complex designs will require the services of an expert.
Conversion to CNC Compatible Format
The next stage is to convert the electronic design to a language the machine understands. You do this using CAM software such as Mastercam, solidCAM, or CAMWorks. The CAM software checks if the model has any mistakes, makes directions for the turning tool, and sets necessary machine parameters.
Prepare the CNC Turning Machine
Before carrying out the turning operation, you must set up and configure the machine. Despite the automation, an operator plays a crucial role in preparing the CNC turning lathe. To do this,
- Put off the machine and load the workpiece onto the chuck.
- Thereafter, select the tools and secure them on the tool turret.
- Calibrate by setting the tools and workpiece correctly.
- Check and optimize necessary parameters.
- Upload the CNC code and prepare for the turning operation.
Note: a low turning speed and high feed rate is better for a rough shape. For smoother finishes and parts with precise tolerance requirements, go for a high turning speed and a lower feed rate.
Produce the CNC Turned Parts
Now, it’s time to bring your idea back to life. There are many turning operations one can use. As soon as you execute the program, the machine runs continuously till the program ends or it is switched off. The loading, cutting, and idle time determines the turning cycle time. You may need to run the machine more than once. This depends on the complexity of the part.
Types of CNC Turning Operations

CNC lathe machining operations can either be internal or external. External operations act on the outer diameter of the workpiece while internal operations work on the internal diameter. However, it is more difficult to carry out internal operations. It causes more chips to build up and requires longer tools.
Let’s examine both categories of CNC operations in detail
External Turning Operations(Specific)
Turning
In the turning process, the tool gradually removes material along the side of the workpiece intending to reduce the outer diameter. This operation can either be rough or finish. In rough turning, the final parts are accurate with a rough surface finish. However, the surface of the final part in the finish turning is fine and glossy. Furthermore, the turned part’s surface can have several features. It can range from steps and tapers to chamfers and contours.
Hard Turning
Hard turning is similar to normal CNC turning operations. However, experts reserve it for hardened steel with hardness values ranging from 58 Rc to 68 Rc. The single-point insert produces precise parts that meet industries’ tight tolerances. Hard turning is an alternative to CNC grinding. Compared to grinding, hard turning is efficient, faster, and cost-effective.
Facing
Many times, a workpiece is usually longer than how it should be. Face turning aims to reduce a part’s length. In facing, the end of the workpiece is located perpendicularly to the rotating axis and moves against the tool. This process smoothens the part as it produces the desired length.
Grooving
The grooving operation involves creating a narrow cut in a workpiece. The size of the cut is related to the width of the cutting tool. The wider the tool, the larger the groove it can produce. Very large grooves require multiple passes and a longer time. Note that the groove can either be located externally or on the surface of the workpiece.
Parting
In parting, the cutting tool moves radially into the side of the workpiece. As it reaches the inner diameter or core, it parts or cuts off a section of the raw material. This operation is for parts one has machined to the required shape and size.
Internal Turning Operations (Non-specific)
Boring
Boring involves rotating a predrilled workpiece over an insert. As the part spins, the insert cuts into the edges of the hole to create a variety of features. Boring operations help to expand smaller holes, straighten holes, and mask die casting defects.
Drilling
Drilling uses a drill bit to cut holes into a workpiece by slowly removing excess materials. The size of the drilling tool will determine the diameter of the hole. It is important to properly calibrate the CNC lathe machine to ensure accuracy.
Threading
This operation uses a specialized threading tool with an indexable insert that moves axially along the side of the workpiece. This tool has a 60-degree pointed noise that cuts threads on outer surfaces. The threads are of varying lengths and some may require more than a single pass.
Knurling
Knurling operation on a CNC lathe machine creates patterned ridges on a metal workpiece. These serrated patterns are functional as they enhance grip. It can also serve aesthetic purposes to improve a part’s appearance.
Reaming
Reaming uses specialized tools to enlarge pre-drilled holes and improve their surface finish. It is similar to boring and drilling. However, it removes a smaller amount of material and acts mainly as a post-processing technique.
Types of CNC Turning Machines
You can use four major CNC turning machine types for your project. They include
Horizontal Turning Centers
It is an enclosed machine that uses a horizontal spindle axis. As the workpiece rotates, the cutting tool shapes it. It is more suitable for longer and cylindrical parts. This CNC turning center does not benefit from gravity. As a result, chips accumulate around the cutting tools and may be challenging to remove. This machine type has applications in manufacturing precision tools and customized auto parts.
Vertical Turning Centers
Here, the workpiece is on a vertical spindle. The cutting tool also works vertically to machine the part in an upward or downward direction. This type is appropriate for complex parts as it incorporates additional milling and drilling functions. It has a widespread use in structural applications and creating prototypes for experimental purposes. The vertical direction of this machine type aids easy removal of chips and makes tool changes faster.
Horizontal Lathes
Here, the workpiece is placed parallel to the ground because the spindle is in a horizontal position. This machine has a small bearing capacity and limited rigidity making it suitable for small to medium-sized components. It achieves tight tolerances when producing electrical fittings and medical equipment.
Vertical Lathes
In contrast to horizontal lathes, the spindle here is in a vertical position. It is a perfect option for shops with limited space. This machine has an excellent weight-carrying capacity making it suitable for heavy components such as marine and wind turbine parts. The vertical setup adds flexibility to machining practices, adapting to different spatial and weight requirements.
Components of CNC Turning Machine
It is important to understand how each part of a CNC turning machine works to achieve the greatest outcome. The following identifies CNC lathes for what they are
Headstock
The headstock is the powerhouse of a CNC turning machine. It houses the spindle that rotates the workpiece. The headstock moves along the X-axis and is at the left side of the machine. It determines the maximum workpiece diameter that can be worked on.
Tailstock
The tailstock is on the opposite end of the headstock and moves the same axis. Its primary function is to support long workpieces and prevent them from deflecting away.
Spindle
Experts refer to the spindle as the backbone of the CNC lathe machine. It secures and rotates the workpiece. Most machines have a single spindle. However, some have more than one to complete a machining operation.
Chuck
The chuck is an important part of the machine as it holds the workpiece as you work on it. Chuck is attached to the headstock and rotated by the spindle. As it rotates, the workpiece removes in the same direction.
Lathe Bed
This is the base of the machine where one mounts the workpiece. It serves as a foundation that supports and connects other components. Usually, it comes with holes that the machinist can use to attach work-holding jigs. This ensures the workpiece remains in place to avoid mistakes.
Carriage
The carriage mounts and controls the movement of the turning tool. It holds the tool turret up and guides it against the workpiece. The main parts of a carriage are the turret, cross slide, and saddle. The carriage moves along the bed with respect to the workpiece.
Tool Turret
Tool turrets are the tool holders. They can hold multiple tools at the same time in the right order. This allows for quick changes between cutting tools and it reduces the number of steps needed to process a part.
Control Panel
This is the brain behind all CNC turning operations. The control panel interprets the G-code and translates it to instructions. It determines the tool’s position and enables the operator to adjust programs before initiating the machining process.
Advantages of CNC Turning
There are many advantages of the CNC turning process which include
- CNC turning produces accurate parts as it eradicates human errors by using CAD and CAD software.
- Turning centers offer flexibility in manufacturing as it is compatible with many materials and different sizes of parts.
- CNC lathes are efficient and fast allowing parts to get to market on time without compromising quality.
- Additionally, CNC turning is a precise method as it ensures consistency in production batches.
- Turning machining is a safe process because it is fully enclosed and prevents materials from flying away and around.
Disadvantages of CNC Turning
Despite the numerous benefits, CNC turning has some shortcomings. The following are some disadvantages of turning parts manufacturing process
- The cost of setting up and maintaining a CNC turning machine is high.
- CNC lathe machining comes with size restrictions and may not be able to accommodate very large workpieces.
- Because the turning process is a subtractive method, it generates a considerable amount of waste.
What are the Most Appropriate Materials for CNC Turning?
CNC turning can work with a variety of materials to give high-quality final parts. Different materials require specific considerations in terms of turning speed, feed rate, and tooling. Here’s a breakdown of some common precision CNC turning materials:
Metals
Most CNC-turned parts are made from metals because they are hard and can withstand the rigors of the operation. Machinists often use brass, aluminum, titanium, and steel.
Plastics
Plastics such as nylon, ABS, PTFE, and acrylic have applications in CNC turning. They are lightweight, strong, and easy to work on.
Wood
Precision CNC turning can also machine wood materials including walnut, oak, and maple. This process creates detailed artistic woodwork with a flawless finish.
Glass
While glass may not be as common as other materials, it is feasible for certain CNC turning applications. With the right parameters, it is possible to machine different types of glass with varying thicknesses.
Wax
Wax finds application in prototyping when using CNC turning processes. It is cost-effective and easy to cut through to make detailed rapid prototypes.
Applications of CNC Turning
CNC turning is an important process in the manufacturing sector. Almost all cylindrical and conical-shaped parts are the result of the process. This section will briefly discuss some industries that rely heavily on CNC turning
Aerospace Components
CNC turning has revolutionized the aerospace industry. It is an invaluable method because it manufactures lightweight aerospace components with zero margins for errors. Manufacturers use turning machining when producing threads, screws, shafts, connector pins, and nuts.
Automotive Parts
Turning machining plays a crucial role in the automotive industry. It is repeatable, leads to speed in production, and boosts sales. CNC lathes are useful when manufacturing auto parts like cylinder blocks and dashboard components.
Electronic Industry
Because it does not require specialized tooling, CNC turning helps in producing parts in the electronic industry within a short time frame. It is compatible with both metals and plastics to create study electronic components.
Oil and Gas Industry
Precision CNC turning helps in manufacturing, repairing, and maintaining parts of the heavy machines in the oil and gas industry. It is the most reliable and precise method when manufacturing parts such as pins, pistons, rods, and cylinders.
Why Use Zintilon for Your CNC Turning Services?
After deciding if CNC turning is the most suitable for your project, the next step is to look for a trusted partner to help bring your ideas to life. From rapid prototyping to mass production, we are here to support every step of your product development.
Zintilon has skilled engineers and machinists who ensure that your parts meet the highest quality standards. We’ve been in business for over 20 years and have served more than 3000 customers across various manufacturing industries. We are versatile as we work with a variety of materials with a lead time as short as 12 hours. Upload your CAD files and get an quote within a day.
Conclusion
CNC turning is crucial in the manufacturing business, providing precision and versatility for a wide range of components. This article has explained the different turning machine types available, CNC turning operations, and their pros and cons. Please reach out if you have questions on anything CNC machining.
FAQs
What are the key parameters of CNC turning?
Some parameters determine the outcome and CNC turning operations. They include cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut, tool geometry, coolant flow, and spindle speed.
What are the tools used in CNC turning?
Common tools of CNC turning are turning tools, boring bars, parting blades, thread-cutting tools, and reamers.
How much does CNC turning cost?
The cost of purchasing and setting up a CNC turning system varies. It covers the expenses incurred from the machines, software tools, tooling costs, energy consumption, and labor costs.
How does CNC turning and milling compare?
Though turning and milling are popular CNC machining techniques. Despite their similarities, they differ in many ways. In CNC milling, it is the cutting tool that rotates to shape a stationary workpiece. This makes it ideal for irregular and flat surfaces.
Great, Together


